Synthesis of polycyclic furan and chromene derivatives via cascade reactions enabled by cleavage of multiple C(sp3)-F bonds
Ting Xie,a Chen Zhang,a Si-Xuan Zhang,a Weidong Rao,b Haiyan Xu,c Zhi-Liang Shen,*a and Xue-Qiang Chu*a
a Technical Institute of Fluorochemistry (TIF), Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing 211816, People’s Republic of China.
b Jiangsu Provincial Key Lab for the Chemistry and Utilization of Agro-Forest Biomass, College of Chemical Engineering, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing 210037, People’s Republic of China.
c School of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, Jiangsu 212003, People’s Republic of China.
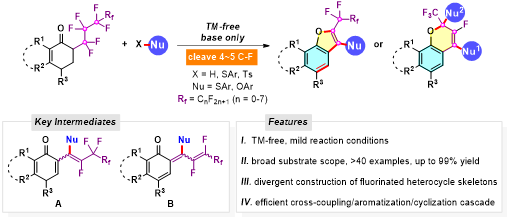
Abstract: The strong and unreactive C-F bond makes polyfluorocarbons extremely long-lived and potentially toxic. A successive selective and controllable C(sp3)-F functionalization of polyfluoroalkylated ketones with S- and O-nucleophiles to enable efficient synthesis of pharmaceutically important fluorine- and sulfur-containing polycyclic furan and chromene derivatives under transition metal-free conditions is demonstrated here. The combination of C-S/C-O coupling, aromatization, and cyclization cascade contribute to the accurate four/five C(sp3)-F bond cleavage at two different sites of perfluoroalkyl chain. The formation of reactive quinoid intermediates and the necessity of using TBAB (tetrabutylammonium bromide) as additive and Cs2CO3 as base were identified by detailed mechanistic studies.
Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, DOI: 10.1002/adsc.202000660 (Impact factor: 5.851).
论文链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/adsc.202000660
