Catalytic enantioselective reductive domino alkyl arylation of acrylates via nickel/photoredox catalysis
Pengcheng Qian1,5, Haixing Guan1,2,5, Yan-En Wang3, Qianqian Lu1, Fan Zhang1, Dan Xiong1, Patrick J. Walsh 4*, Jianyou Mao1*
1 Institute of Advanced Synthesis, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, 30 South Puzhu Road, Nanjing 211816, P.R. China
2 Experimental Center, Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Classical Theory, Ministry of Education, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, PR China
3 College of Science, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, PR China
4 Roy and Diana Vagelos Laboratories, Department of Chemistry, University of Pennsylvania, 231 South 34th Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104-6323, United States
5 These authors contributed equally: Pengcheng Qian, Haixing Guan
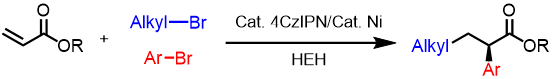
Abstract: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug derivatives (NSAIDs) are an important class of medications. Here we show a visible-light-promoted photoredox/nickel catalyzed approach to construct enantioenriched NSAIDs via a three-component alkyl arylation of acrylates. This reductive cross-electrophile coupling avoids preformed organometallic reagents and replaces stoichiometric metal reductants by an organic reductant (Hantzsch ester). A broad range of functional groups are well-tolerated under mild conditions with high enantioselectivities (up to 93% ee) and good yields (up to 90%). A study of the reaction mechanism, as well as literature precedence, enabled a working reaction mechanism to be presented. Key steps include a reduction of the alkyl bromide to the radical, Giese addition of the alkyl radical to the acrylate and capture of the α-carbonyl radical by the enantioenriched nickel catalyst. Reductive elimination from the proposed Ni(III) intermediate generates the product and forms Ni(I).
Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6613 (2021年影响因子: 14.919).
论文链接:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-26794-8?utm_source=xmol&utm_medium=affiliate&utm_content=meta&utm_campaign=DDCN_1_GL01_metadata#citeas
