A Novel Synthesis of β-CD@SA@Ag Composite Hydrogel Microspheres with High Catalytic Activity and Environmental Adaptability
Xiang-Hua Ling, Yue-Feng Tang and Guo-Zhi Han*
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211816, P.R. China
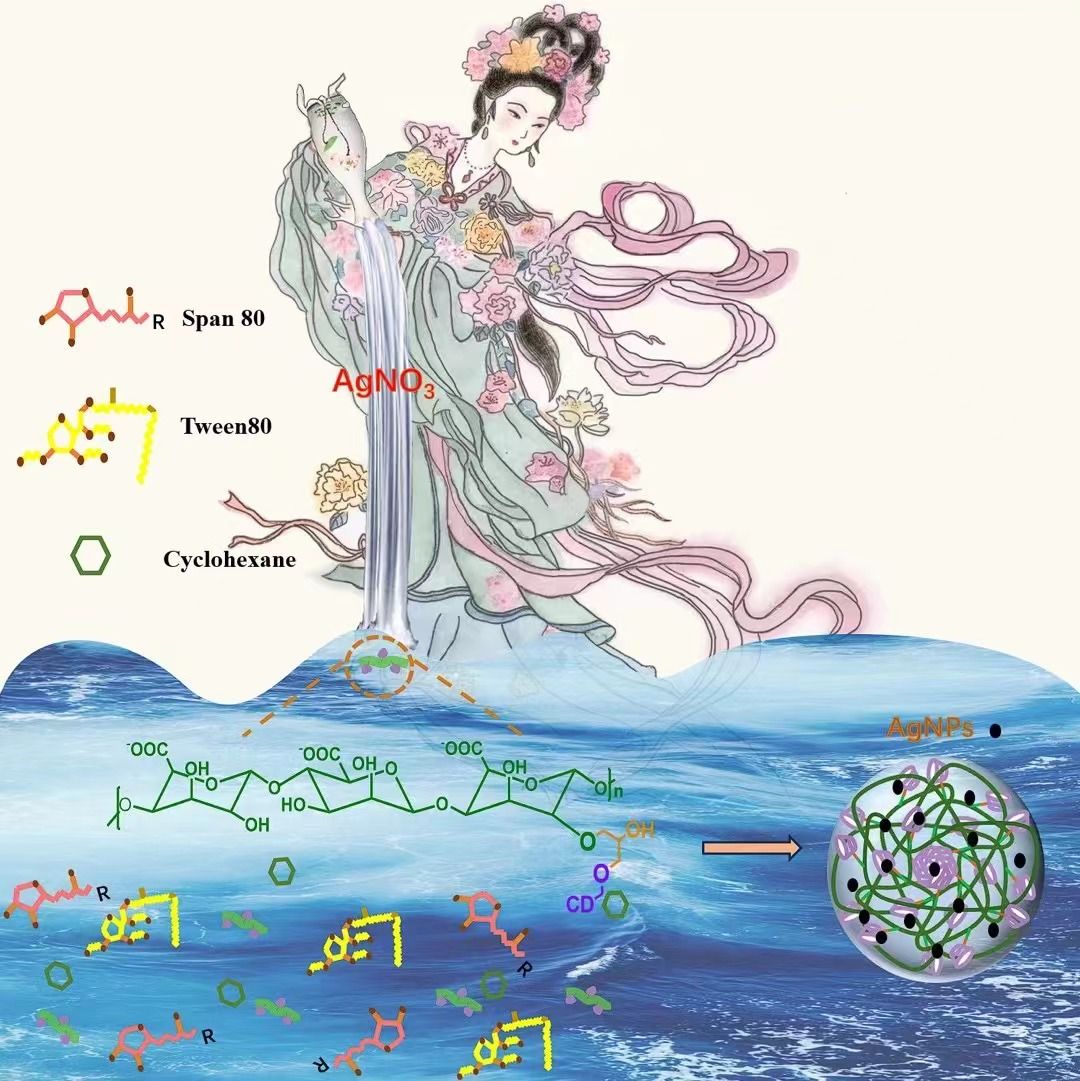
Abstract: In this paper, we developed a novel and green strategy to synthesize a kind of composite hydrogel microspheres containing silver nanoparticles and β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) modified sodium alginate (β-CD@SA@Ag) without use of strong reducing reagent. First, β-CD was chemical linked to SA by epichlorohydrin (ECH) to form the β-CD modified polymer (β-CD@SA). then AgNO3 was added to the as-prepared polymer solution, in which silver nanoparticles were formed by the reducing power of β-CD units. Subsequently, by reversed-phase emulsion method and ionic cross-linking, a kind of β-CD@SA@Ag hydrogel microspheres were obtained. Test data indicated that silver nanoparticles evenly dispersed in the composite material. On the basis, the adsorption and catalytic performances of the β-CD@SA@Ag hydrogel microspheres were studied towards to the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. Research results showed that the β-CD@SA@Ag hydrogel microspheres had excellent catalytic activity along with high environmental adaptability. whether in pure water, tap water or river water, aromatic nitro compounds can be completely reduced within 2-13 minutes. Moreover, the morphology of microspheres of the composite material endows the composite material with high stability and reusability. We believe that our work would provide a new idea for the green synthesis of organic-inorganic composite functional materials.
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2024,683,133078 (IF=5.2)
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.133078
