金属团簇的结构控制及其在能源和环境催化中的应用
报告人:Yuichi NEGISHI(日本东北大学教授)
时间:2024.12.27(周五)上午10:00
地点:化学学科楼报告厅A400
报告人简介:
•教育背景:1996年、1998年分别获得庆应义塾大学理学学士、理学硕士学位,2001年于庆应义塾大学获得博士学位,导师为 Koji Kaya 教授和 Atsushi Nakajima 教授。
•研究领域:物理化学、团簇化学、纳米材料化学。
•学术成就:在J. Am. Chem. Soc.、Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.、 Coord. Chem. Rev.、Acc. Chem. Res.等期刊发表了275篇高影响力的学术论文,H-inde达到61。多次获得重要奖项,包括2023年向井奖、2022年日本化学会创造性工作奖、2020年日本分子科学会国际研究者奖、2018年由国际纯粹与应用化学联合会颁发的新型材料及其合成杰出奖,以及日本分子科学会青年科学家奖、日本化学会青年化学家奖、纳米科学与技术学会最佳青年报告者奖、英国皇家化学会物理化学和化学物理领域杰出青年化学家PCCP奖等。
报告摘要:
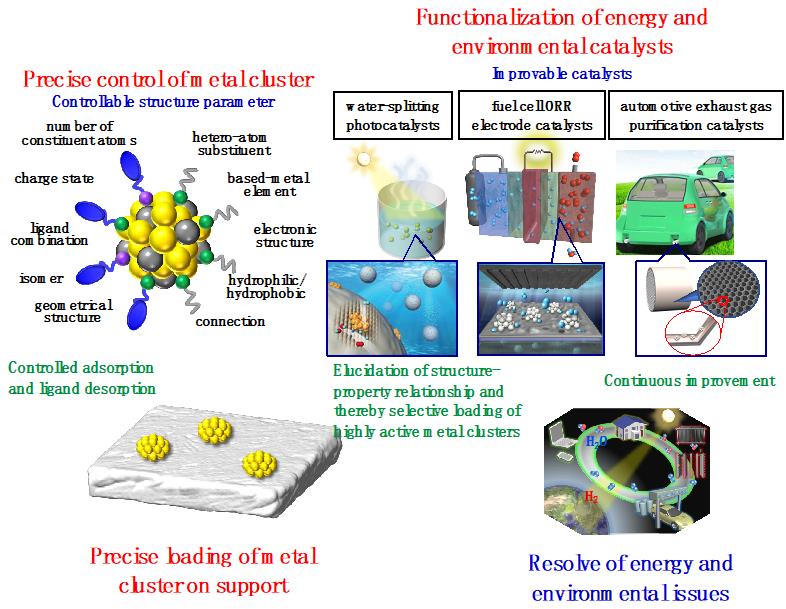
To build a sustainable society, new innovative materials are needed. Nanoscale structure control of materials can lead to such creations. Ultrafine metal clusters with a few to dozens of metal atoms have unique electronic/geometric structures and properties different from bulk metals of the same elements. Doping different elements into these clusters creates diverse structures, properties, and functions, making them potential units for innovative materials.
To understand and apply metal clusters, it's essential to control their chemical composition and geometric structure. We have developed techniques for this control and a method to control supported metal clusters to enhance the functionality of water-splitting photocatalysts, fuel cell electrocatalysts, and automotive exhaust gas purifying catalysts.
We have achieved the highest water-splitting activity for UV-responsive BaLa4Ti4O15 photocatalysts, created platinum electrocatalysts with better oxygen-reduction activity than current fuel cell ones, and developed highly functional automotive exhaust gas purification catalysts. Our research uniquely achieves atomic-level control of metal clusters from synthesis to support control. This presentation summarizes our recent related work.